|
Need a JOB?













Top Search Engines










Linux Resources
















Virus Scan Online








| |
My reviewers and technical notes
NOTICE: The following procedure/reviewer contains here are all free and you can do
whatever you want with it. But I do not guarantee success or
support these actions. Any use of the information provided herein, is
performed at your own risk. You should make a backup copy of your files
prior to executing any of the following steps. Incorrect use of the
instructions can cause serious problems that may require a complete
reinstall of your operating system. I assumes no responsibility, expressed
or implied, regarding the consequences of any action taken as a result of
the information provided herein.
NAV Unable to Initialize Virus Scanning Engine Database
IE issues
Error: " The Print Spooler or one of its dependencies is not available. "
helpful sites
cd_dvd_hdd_fdd issues
how do I Start Computer in SafeMode
windows support page
how to install lexmark printer?
MS outlook issues
PRINTERS/SCANNERS/CAMERA
CDs not autorun when inserted in my CD/DVD drive in the MS Windows XP OS?
A+ Certification
Starting up and shutting down
Windows 2000 Pro Amalgamation Braindump
Network Admin_1
CDs not autorun when inserted in CD/ DVD drive in the MS Windows2000 or NT OS?
Internetworking Technologies
RAID LEVELs
Internetworking Acronyms
How do I troubleshoot a computer running Windows® 95/98 when it will not boot to the hard drive?
DVD media may not ‘Autoplay’ in Windows XP Home/Pro
Shells and stuff
X linux partitions and disk mgmnt
315 from a Millionaire
Bartleby Quotes of the Day
Vocabulary 6
Civil Service Reviewer
Internet acronyms
Vocabulary 1
Vocabulary 10
Bible quiz
DELL P1500 and S2500 Printers, Adding & setting up an optional paper tray
90-90 Diags
MSWord Tips
guide to subnetting
TCP/IP basics
having a successful job interview
RAID-Definitions
|
 |
|
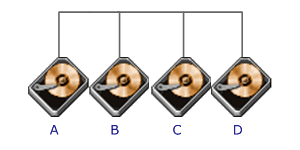
RAID
Level 0 requires a minimum of 2 drives to implement |
|
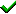 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
RAID 0
implements a striped disk array, the data is broken down into blocks and
each block is written to a separate disk drive
No parity calculation overhead is involved
Very simple design
Easy to implement |
Not a
'True' RAID because it is NOT fault-tolerant
The failure of just one drive will result in all data in an array being lost
Should never be used in mission critical environments |
|
 |
|
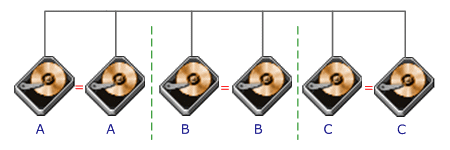
RAID
Level 1 requires a minimum of 2 drives to implement |
|
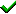 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
One
Write or two Reads possible per mirrored pair
100% redundancy of data means no rebuild is necessary in case of a disk
failure, just a copy to the replacement disk
Simplest RAID storage subsystem design |
Highest
disk overhead of all RAID types (100%) - inefficient
Typically the RAID function is done by system software, loading the
CPU/Server and possibly degrading throughput at high activity levels.
Hardware implementation is strongly recommended. |
|
 |
|
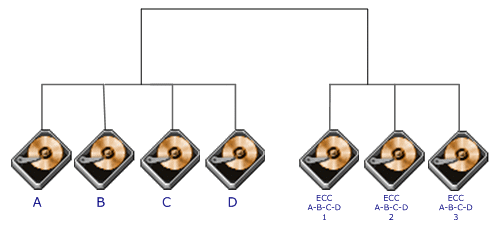
Each
bit of data word is written to a data disk drive (4 in this example: 0 to
3). Each data word has its Hamming Code ECC word recorded on the ECC disks.
On Read, the ECC code verifies correct data or corrects single disk errors. |
|
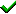 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
'On the
fly' data error correction
Extremely high data transfer rates possible
The higher the data transfer rate required, the better the ratio of data
disks to ECC disks |
Very
high ratio of ECC disks to data disks with smaller word sizes - inefficient
Entry level cost very high - requires very high transfer rate requirement to
justify.
No commercial implementations exist. |
|
 |
|
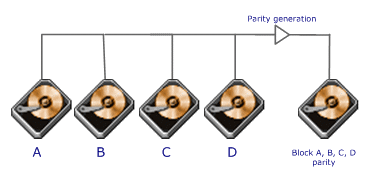
The
data block is subdivided ('striped') and written on the data disks. Stripe
parity is generated on Writes, recorded on the parity disk and checked on
Reads.
RAID Level 3 requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement |
|
 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
Very
high Read data transfer rate
Very high Write data transfer rate
Disk failure has an insignificant impact on throughput
Low ratio of ECC (Parity) disks to data disks means high efficiency |
Transaction rate equal to that of a single disk drive at best (if spindles
are synchronized)
Controller design is fairly complex
Very difficult and resource intensive to do as a 'software' RAID |
|
 |
|
Each
entire block is written onto a data disk. Parity for same rank blocks is
generated on Writes, recorded on the parity disk and checked on Reads.
RAID Level 4 requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement |
|
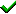 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
Very
high Read data transaction rate
Low ratio of ECC (Parity) disks to data disks means high efficiency
High aggregate Read transfer rate
Low ratio of ECC (Parity) disks to data disks means high efficiency |
Quite
complex controller design
Worst Write transaction rate and Write aggregate transfer rate
Difficult and inefficient data rebuild in the event of disk failure
Block Read transfer rate equal to that of a single disk |
|
 |
|
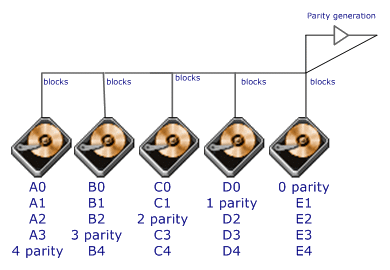
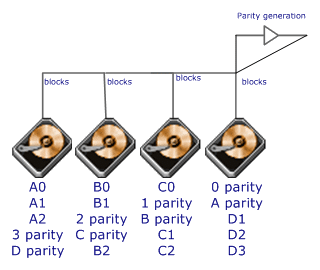
Each
entire data block is written on a data disk; parity for blocks in the same
rank is generated on Writes, recorded in a distributed location and checked
on Reads.RAID Level 5 requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement |
|
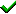 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
Highest
Read data transaction rate
Medium Write data transaction rate
Low ratio of ECC (Parity) disks to data disks means high efficiency
Good aggregate transfer rate |
Disk
failure has a medium impact on throughput
Most complex controller design
Difficult to rebuild in the event of a disk failure (as compared to RAID
level 1)
Individual block data transfer rate same as single disk |
|
 |
|
Each
entire data block is written on a data disk; parity for blocks in the same
rank is generated on Writes, recorded in a distributed location and checked
on Reads.RAID Level 5 requires a minimum of 3 drives to implement |
|
 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
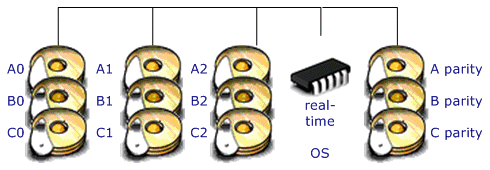
RAID 6
is essentially an extension of RAID level 5 which allows for additional
fault tolerance by using a second independent distributed parity scheme
(two-dimensional parity)
Data is striped on a block level across a set of drives, just like in RAID
5, and a second set of parity is calculated and written across all the
drives; RAID 6 provides for an extremely high data fault tolerance and can
sustain multiple simultaneous drive failures
Perfect solution for mission critical applications |
Very
complex controller design
Controller overhead to compute parity addresses is extremely high
Very poor write performance
Requires N+2 drives to implement because of two-dimensional parity scheme |
|
 |
|
Fully
implemented process oriented real time operating system resident on embedded
array control microprocessor.
RAID 7 is a registered trademark of Storage Computer Corporation. |
|
 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
Overall
write performance is 25% to 90% better than single spindle performance and
1.5 to 6 times better than other array levels
Host interfaces are scalable for connectivity or increased host transfer
bandwidth
Small reads in multi user environment have very high cache hit rate
resulting in near zero access times
No extra data transfers required for parity manipulation |
One
vendor proprietary solution
Extremely high cost per MB
Very short warranty
Not user serviceable
Power supply must be UPS to prevent loss of cache data |
|
 |
|
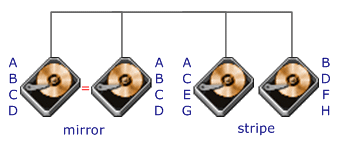
RAID
Level 10 requires a minimum of 4 drives to implement |
|
 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
RAID 10
is implemented as a striped array whose segments are RAID 1 arrays
RAID 10 has the same fault tolerance as RAID level 1
RAID 10 has the same overhead for fault-tolerance as mirroring alone
Excellent solution for sites that would have otherwise gone with RAID 1 but
need some additional performance boost |
Very
expensive / High overhead
All drives must move in parallel to proper track lowering sustained
performance
Very limited scalability at a very high inherent cost |
|
 |
|
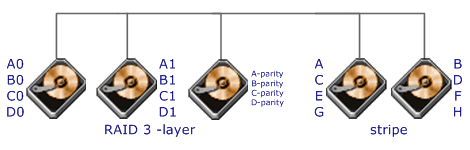
RAID
Level 53 requires a minimum of 5 drives to implement |
|
 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
RAID 53
should really be called 'RAID 03' because it is implemented as a striped
(RAID level 0) array whose segments are RAID 3 arrays
RAID 53 has the same fault tolerance as RAID 3 as well as the same fault
tolerance overhead
High data transfer rates are achieved thanks to its RAID 3 array segments
Maybe a good solution for sites who would have otherwise gone with RAID 3
but need some additional performance boost |
Very
expensive to implement
All disk spindles must be synchronized, which limits the choice of drives
Byte striping results in poor utilization of formatted capacity |
|
 |
|
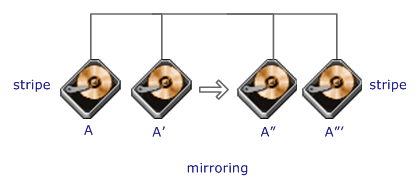
RAID
Level 0+1 requires a minimum of 4 drives to implement |
|
 Advantages Advantages |
 Disadvantages Disadvantages |
|
RAID
0+1 is implemented as a mirrored array whose segments are RAID 0 arrays
RAID 0+1 has the same fault tolerance as RAID level 5
RAID 0+1 has the same overhead for fault-tolerance as mirroring alone
Excellent solution for sites that need high performance but are not
concerned with achieving maximum reliability |
RAID
0+1 is NOT to be confused with RAID 10. A single drive failure will cause
the whole array to become, in essence, a RAID Level 0 array
Very expensive / High overhead
Very limited scalability at a very high inherent cost
All drives must move in parallel to proper track lowering sustained
performance |
back on top
(c)
Advanced Computer &
Network Corporation
| |




Submit your site to 20 popular
Search Engines for FREE!
| |
| |
Dream dictionary







Family Links






|